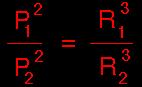Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion
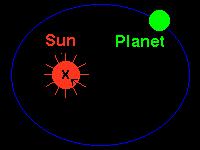
1st Law of Planetary Motion
Kepler established that the orbits of plants are ellipses
and not circles. The sun is located at one foci, and the planet travels
along the line of the ellipse.
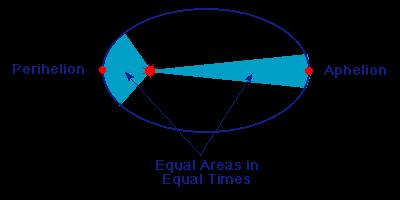
2nd Law of Planetary Motion
Kepler stated that if lines were drawn out to the planet
on either sides of the ellipse, the area and time on either side
would be equal. Since the arc length is longer closer to the sun
it must move faster in order to cover the same amount of area as the opposite
side. The terms perihelion refers to the side closer to the sun,
and the term aphelion refers to the side of the ellipse farthest from the
sun.
3rd Law of Planetary Motion
This law states that the square of the orbital period
of any two planets is proportional to the cube of the semi major axis of
the elliptical orbit. This equation can be used to derive orbital
periods of planets.